当前位置:网站首页>我们编写 React 组件的最佳实践
我们编写 React 组件的最佳实践
2020-11-06 01:23:01 【:::::::】
刚接触 React 的时候,在一个又一个的教程上面看到很多种编写组件的函数,尽管那时候 React 框架已经相当成熟,但是并没有一个固定的规则去规范我们去写代码。
在过去的一年里,我们在不断的完善我们的做法,直到满意为止。
本文会列出我们自己在使用的最佳实践,不管你是刚入门的新手还是很有经验的开发者,我们都希望本文对你有所帮助。
开始之前,先列几条:
- 我们使用ES6/ES7
- 如果你无法区分页面组件和容器组件,推荐阅读 这篇文章
- 如果有更好的意见或建议,请在评论区告诉我,谢谢
基于 Class 的组件
基于 Class 的组件是有状态的,不管它包不包含函数,我们都会尽量少用。但是它也有它的用处。
现在来一行一行的编写我们的组件:
导入 CSS
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import ExpandableForm from './ExpandableForm'
import './styles/ProfileContainer.css'
我喜欢 CSS in Javascript,但是这个概念还比较新,现在也并没有成熟的解决方案,所以我们在每个组件里面去引用 CSS
初始化 State
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import ExpandableForm from './ExpandableForm'
import './styles/ProfileContainer.css'
export default class ProfileContainer extends Component {
state = { expanded: false }
当然你也可以选择在构造函数里面去初始化,但是我们觉得这种方式更加清晰。
当然也会保证 Class 是默认导出的。
propTypes 和 defaultProps
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { string, object } from 'prop-types'
import ExpandableForm from './ExpandableForm'
import './styles/ProfileContainer.css'
export default class ProfileContainer extends Component {
state = { expanded: false }
static propTypes = {
model: object.isRequired,
title: string
}
static defaultProps = {
model: {
id: 0
},
title: 'Your Name'
}
propTypes 和 defaultProps 是静态属性,尽可能的把它们写在组件的最上方,以便其他开发者阅读。
如果使用 React 15.3.0 或更高的版本,使用 prop-types 代替 React.PropTypes
所有的组件都必须声明 propTypes
函数
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { string, object } from 'prop-types'
import ExpandableForm from './ExpandableForm'
import './styles/ProfileContainer.css'
export default class ProfileContainer extends Component {
state = { expanded: false }
static propTypes = {
model: object.isRequired,
title: string
}
static defaultProps = {
model: {
id: 0
},
title: 'Your Name'
}
handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
this.props.model.save()
}
handleNameChange = (e) => {
this.props.model.changeName(e.target.value)
}
handleExpand = (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
this.setState({ expanded: !this.state.expanded })
}
使用基于 Class 的组件时,当你传递函数给子组件的时候,要确保他们有正确的 this,通常用这种形式实现 this.handleSubmit.bind(this)
但是如果你使用箭头函数,就不需要 bind(this)
为 setState 传递函数
上面的例子中我们是这么做的:
this.setState({ expanded: !this.state.expanded })
这里有个 setState 的小知识 —— 它是异步的,为了保证性能,React 会分批修改 state,所以 state 不会在调用 setState 之后立即改变
这意味着你不能依赖当前的状态,因为你不知道当前的状态是什么状态
这里有个解决方案 —— 传递函数给 setState,React 会把上一个状态 prevState 传递给你
this.setState(prevState => ({ expanded: !prevState.expanded }))
解构 Props
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { string, object } from 'prop-types'
import ExpandableForm from './ExpandableForm'
import './styles/ProfileContainer.css'
export default class ProfileContainer extends Component {
state = { expanded: false }
static propTypes = {
model: object.isRequired,
title: string
}
static defaultProps = {
model: {
id: 0
},
title: 'Your Name'
}
handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
this.props.model.save()
}
handleNameChange = (e) => {
this.props.model.changeName(e.target.value)
}
handleExpand = (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
this.setState(prevState => ({ expanded: !prevState.expanded }))
}
render() {
const {
model,
title
} = this.props
return (
<ExpandableForm
onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}
expanded={this.state.expanded}
onExpand={this.handleExpand}>
<div>
<h1>{title}</h1>
<input
type="text"
value={model.name}
onChange={this.handleNameChange}
placeholder="Your Name"/>
</div>
</ExpandableForm>
)
}
}
像上面的例子一样,每个 prop 都独占一行
装饰器(Decorators)
@observer
export default class ProfileContainer extends Component {
如果你使用了类似 mobx 的库,你可以这样去装饰你的 Class 组件
修改函数式组件使用 decorators 很灵活并且可读
如果你不想使用装饰器,可以这么做:
class ProfileContainer extends Component {
// Component code
}
export default observer(ProfileContainer)
闭包
避免像下面注释的地方一样传递新的闭包给子组件:
<input
type="text"
value={model.name}
// onChange={(e) => { model.name = e.target.value }}
// ^ Not this. Use the below:
onChange={this.handleChange}
placeholder="Your Name"/>
这种方式的好处是每次render,不会重新创建一个函数,没有额外的性能损失。
这里是完整的组件:
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { string, object } from 'prop-types'
// Separate local imports from dependencies
import ExpandableForm from './ExpandableForm'
import './styles/ProfileContainer.css'
// Use decorators if needed
@observer
export default class ProfileContainer extends Component {
state = { expanded: false }
// Initialize state here (ES7) or in a constructor method (ES6)
// Declare propTypes as static properties as early as possible
static propTypes = {
model: object.isRequired,
title: string
}
// Default props below propTypes
static defaultProps = {
model: {
id: 0
},
title: 'Your Name'
}
// Use fat arrow functions for methods to preserve context (this will thus be the component instance)
handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
this.props.model.save()
}
handleNameChange = (e) => {
this.props.model.name = e.target.value
}
handleExpand = (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
this.setState(prevState => ({ expanded: !prevState.expanded }))
}
render() {
// Destructure props for readability
const {
model,
title
} = this.props
return (
<ExpandableForm
onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}
expanded={this.state.expanded}
onExpand={this.handleExpand}>
// Newline props if there are more than two
<div>
<h1>{title}</h1>
<input
type="text"
value={model.name}
// onChange={(e) => { model.name = e.target.value }}
// Avoid creating new closures in the render method- use methods like below
onChange={this.handleNameChange}
placeholder="Your Name"/>
</div>
</ExpandableForm>
)
}
}
函数式组件
这些组件没有状态和函数,他们很纯,非常容易阅读,尽量多的使用他们。
propTypes
import React from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { func, bool } from 'prop-types'
import './styles/Form.css'
ExpandableForm.propTypes = {
onSubmit: func.isRequired,
expanded: bool
}
// Component declaration
这里我们把 propTypes 写在最前面,他会被组件立即可见,这要归功于JavaScript的 函数提升
解构 Props 和 defaultProps
import React from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { func, bool } from 'prop-types'
import './styles/Form.css'
ExpandableForm.propTypes = {
onSubmit: func.isRequired,
expanded: bool,
onExpand: func.isRequired
}
function ExpandableForm(props) {
const formStyle = props.expanded ? {height: 'auto'} : {height: 0}
return (
<form style={formStyle} onSubmit={props.onSubmit}>
{props.children}
<button onClick={props.onExpand}>Expand</button>
</form>
)
}
我们的组件是一个函数,我们获取他的 props 就是在获取函数的参数值,我们可以直接用 ES6 的解构:
import React from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { func, bool } from 'prop-types'
import './styles/Form.css'
ExpandableForm.propTypes = {
onSubmit: func.isRequired,
expanded: bool,
onExpand: func.isRequired
}
function ExpandableForm({ onExpand, expanded = false, children, onSubmit }) {
const formStyle = expanded ? {height: 'auto'} : {height: 0}
return (
<form style={formStyle} onSubmit={onSubmit}>
{children}
<button onClick={onExpand}>Expand</button>
</form>
)
}
我们也可以使用默认参数值去设置 defaultProps,就像上面的 expanded = false
避免使用下面的 ES6 语法:
const ExpandableForm = ({ onExpand, expanded, children }) => {
看起来很先(逼)进(格),但这个函数是匿名的。
如果你的Babel设置正确,这个匿名函数不会成为一个问题 —— 但是如果不是的话,任何错误都会显示在 << anonymous >> 中,这对于调试来说是非常糟糕的。
Wrapping
函数式组件中不能使用 decorators,你只需把它作为参数传递给过去
import React from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { func, bool } from 'prop-types'
import './styles/Form.css'
ExpandableForm.propTypes = {
onSubmit: func.isRequired,
expanded: bool,
onExpand: func.isRequired
}
function ExpandableForm({ onExpand, expanded = false, children, onSubmit }) {
const formStyle = expanded ? {height: 'auto'} : {height: 0}
return (
<form style={formStyle} onSubmit={onSubmit}>
{children}
<button onClick={onExpand}>Expand</button>
</form>
)
}
export default observer(ExpandableForm)
这里是完整的组件:
import React from 'react'
import { observer } from 'mobx-react'
import { func, bool } from 'prop-types'
// Separate local imports from dependencies
import './styles/Form.css'
// Declare propTypes here, before the component (taking advantage of JS function hoisting)
// You want these to be as visible as possible
ExpandableForm.propTypes = {
onSubmit: func.isRequired,
expanded: bool,
onExpand: func.isRequired
}
// Destructure props like so, and use default arguments as a way of setting defaultProps
function ExpandableForm({ onExpand, expanded = false, children, onSubmit }) {
const formStyle = expanded ? { height: 'auto' } : { height: 0 }
return (
<form style={formStyle} onSubmit={onSubmit}>
{children}
<button onClick={onExpand}>Expand</button>
</form>
)
}
// Wrap the component instead of decorating it
export default observer(ExpandableForm)
JSX 中的条件判断
你可能会有很复杂的条件判断语句,但是你要避免下面的写法:
嵌套的三元表达式不是一个好的方法,太难阅读了
有一些库可以解决这个问题(jsx-control-statements),但是我们没有引入其他的库,我们是这么解决的:
我们使用了 立即执行函数 把条件语句写在里面,虽然这样可能会导致性能下降,但是在大多数情况下,它带来的负面影响还是小于糟糕的可读性。
当然如果组件分的足够细,你可能不会用到这么复杂的条件判断。
此外,如果你只在一个表达式里面去渲染组件,避免这么做:
True!
: } title="" data-original-title="复制">
{
isTrue
? <p>True!</p>
: <none/>
}
你可以使用短路语法:
True!
} " title="" data-original-title="复制">
{
isTrue &&
<p>True!</p>
}
总结
这篇文章对你有帮助吗?请在评论区给出你的意见和建议,感谢阅读!
本文首发于我的 个人博客,另外推荐一个我前阵子写的一个脚手架 parcel-typescript-react-boilerplate,请给出意见和建议,相互学习。无耻的求个星,谢谢~~!
本文参与腾讯云自媒体分享计划,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。
版权声明
本文为[:::::::]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1715161
边栏推荐
- C++ 数字、string和char*的转换
- C++学习——centos7上部署C++开发环境
- C++学习——一步步学会写Makefile
- C++学习——临时对象的产生与优化
- C++学习——对象的引用的用法
- C++编程经验(6):使用C++风格的类型转换
- Won the CKA + CKS certificate with the highest gold content in kubernetes in 31 days!
- C + + number, string and char * conversion
- C + + Learning -- capacity() and resize() in C + +
- C + + Learning -- about code performance optimization
猜你喜欢
-
C + + programming experience (6): using C + + style type conversion
-

Latest party and government work report ppt - Park ppt
-
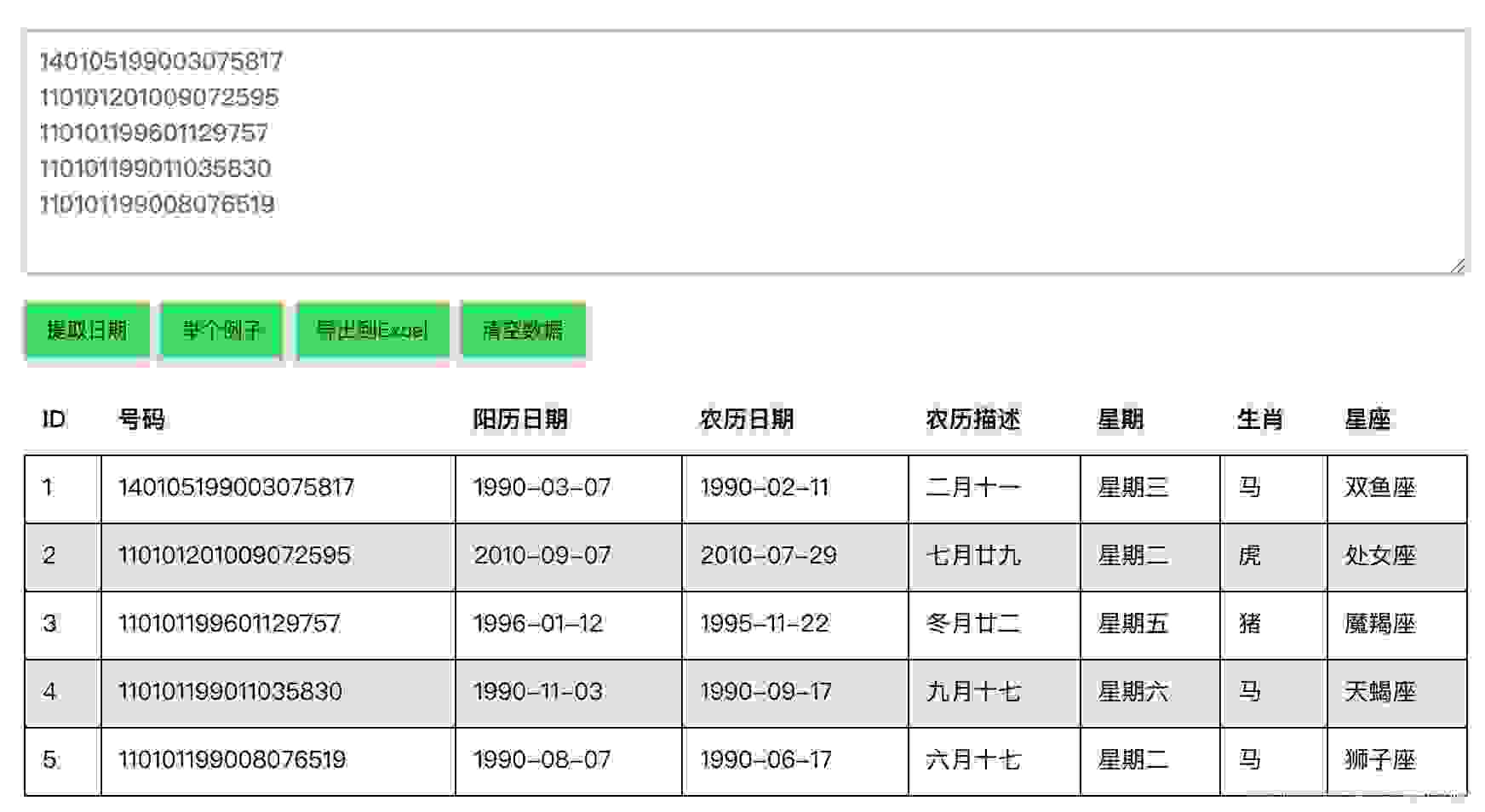
在线身份证号码提取生日工具
-

Online ID number extraction birthday tool
-
️野指针?悬空指针?️ 一文带你搞懂!
-
Field pointer? Dangling pointer? This article will help you understand!
-
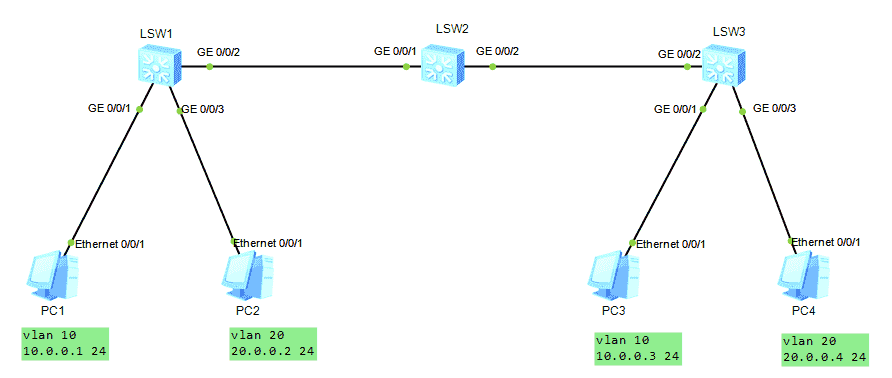
HCNA Routing&Switching之GVRP
-

GVRP of hcna Routing & Switching
-

Seq2Seq实现闲聊机器人
-
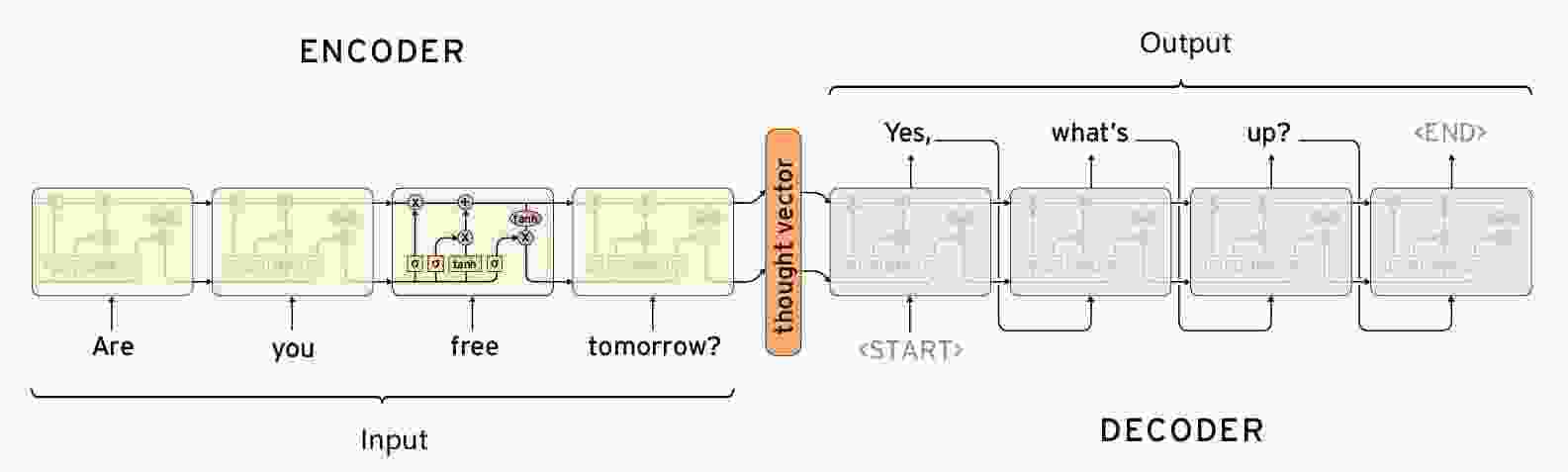
【闲聊机器人】seq2seq模型的原理
随机推荐
- LeetCode 91. 解码方法
- Seq2seq implements chat robot
- [chat robot] principle of seq2seq model
- Leetcode 91. Decoding method
- HCNA Routing&Switching之GVRP
- GVRP of hcna Routing & Switching
- HDU7016 Random Walk 2
- [Code+#1]Yazid 的新生舞会
- CF1548C The Three Little Pigs
- HDU7033 Typing Contest
- HDU7016 Random Walk 2
- [code + 1] Yazid's freshman ball
- CF1548C The Three Little Pigs
- HDU7033 Typing Contest
- Qt Creator 自动补齐变慢的解决
- HALCON 20.11:如何处理标定助手品质问题
- HALCON 20.11:标定助手使用注意事项
- Solution of QT creator's automatic replenishment slowing down
- Halcon 20.11: how to deal with the quality problem of calibration assistant
- Halcon 20.11: precautions for use of calibration assistant
- “十大科学技术问题”揭晓!|青年科学家50²论坛
- "Top ten scientific and technological issues" announced| Young scientists 50 ² forum
- 求反转链表
- Reverse linked list
- js的数据类型
- JS data type
- 记一次文件读写遇到的bug
- Remember the bug encountered in reading and writing a file
- 单例模式
- Singleton mode
- 在这个 N 多编程语言争霸的世界,C++ 究竟还有没有未来?
- In this world of N programming languages, is there a future for C + +?
- es6模板字符
- js Promise
- js 数组方法 回顾
- ES6 template characters
- js Promise
- JS array method review
- 【Golang】️走进 Go 语言️ 第一课 Hello World
- [golang] go into go language lesson 1 Hello World